Binary Sensor Service
Bluetooth Binary Sensor Service Implementation für das Arduino Framework nach Bluetooth® Service Specification V1.0
Development:
- Seeed Studio XIAO-NRF52840
- Visual Studi Code
- Platform.io
- Arduino Framework
- Visual Studio 2022
- Windows dotNet V8.0
Bluetooth® LE
- Bluetooth BSS Spezifikation V1.0
- Full impl, single/multiple Sensors
- BSS impl mit ArduinoBLE
- BSS impl. mit c# Windows LE
- Windows WPF BSS Testsuit
- XIAO-NRF52840
Sensors:
- Seeed Studio XIAO-NRF52840
- Analyse von Piezosignal
- Fenster Glasbruch Erkennung
- Fenster Glasvibration
- Fensterflügel mit Reedkontakt
- Option für Human dedection
Programmbeschreibung
Das BSS Modul beinhaltet die BBS Class mit den BSS Methoden und eine Helperclass Join welche für die Zuammensetzung der aufgeteilten Übertragungsdaten Anwendung findet.
Anwendung und Ablauf Teil BSS Modul
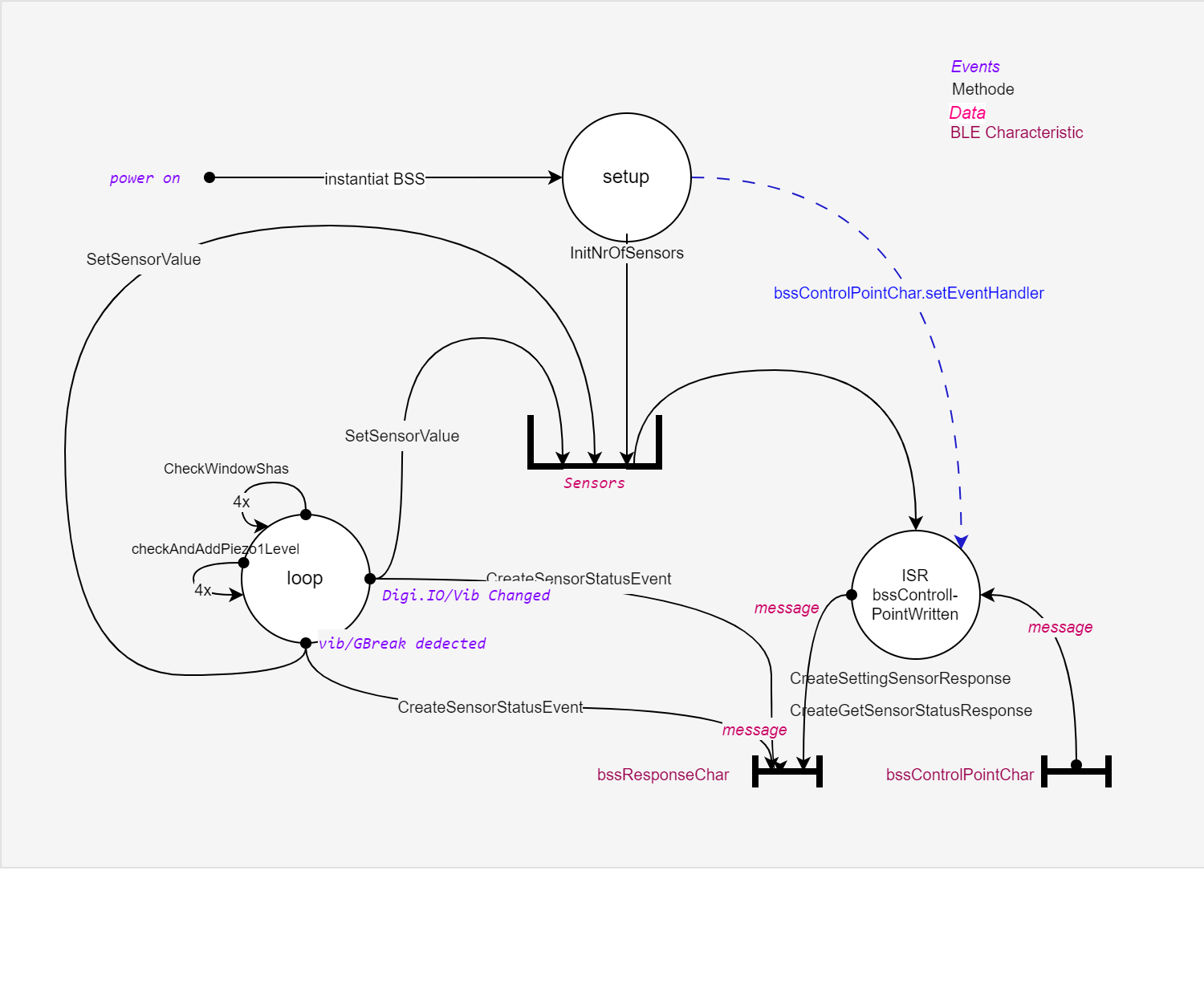
Sensor ist das Data Model und verwaltet alle Sensoren mit aktuellen Werten. Es gibt 3 Sensorlisten für je OCL , VIB und HUM (Open/Close, Vibration und Human).
- OCL sind digitale Eingänge
- OCL virtuell Glas break Sensoren werden aus der Analogwerten eruiert.
- VIB sind virtuelle Sensoren und werden aus der Analogwerten eruiert.
- Hum sind nicht verwendet sind aber als digitale Eingänge angedacht.
- Message ist der Byte stream an Bluetooth und ist max. 256Byte gross.
Vibration werden gesetzt wenn Anzahl und Peak erfüllt sind. Sie werden nach 5sek rückgesetzt.
Glas Break werden gesetzt wenn Anzahl und Peak erfüllt sind. Sie werden nie zurückgesetzt (nur mit reset Pin)
BSS Characteristic
BSS hat zwei Characteristic , bssResponseChar und der bssControlPointChar für die beiden Richtungen von Central nach Peripheral und umgekehrt,
Defs
in BSS.h
/// @brief subtype message header
typedef struct {
byte rfu1;
byte messageId;
byte rfu2;
byte nrOfParameter;
} MsgHdr;
/// @brief subtype message parameter
typedef struct {
byte parameterId;
byte parameterLen;
byte rfu[2];
byte *values;
} MsgParameter;
/// @brief type for building the message
typedef struct {
MsgHdr header;
MsgParameter *parameters;
} msgType;
/// @brief type for the sensormodel
typedef struct {
byte nr;
byte len; // names longer than 31 byte are purged
char *name; // name is not 0 terminate therefor is len needed
byte value; // 1 = open window or vibration dedcted or human dedected
short changes; // mdoulus 2048
} Sensor;
Class BSS
in BSS.h
class BSS {
protected:
byte SplitHeader(byte sequenz, byte last);
public:
BSS(int source);
int InitNrOfSensors(int nrOCS=1, int nrHumS = 0, int nrVibS=0);
bool GetReporting( byte sensorType);
void GetCompressedlSensorValues (byte *pAllSensors) ;
bool SetSensorValue(byte sensorType, byte nr, byte val);
int CreateGetSensorStatusCommand( byte sensorType, BLECharacteristic ch);
int CreateGetSensorStatusResponse(byte sensorType, BLECharacteristic ch);
int CreateSettingSensorCommand( byte sensorType, byte status, String names[], BLECharacteristic ch);
int CreateSettingSensorResponse( byte sensorType, BLECharacteristic ch);
int CreateSensorStatusEvent( byte sensorType, BLECharacteristic ch);
int CreateStopSensorStatusEvent( BLECharacteristic ch);
int DisasemblingControlCommand( byte es, byte msg[], int len);
private:
int _source ; // central or peripheral resp. 0 = from client; 1 = from server
int _totalSensors;
int _sensorReporting;
int _nrOfOCSensors;
int _nrOfVibSensors;
int _nrOfHumSensors;
// following are pointer to SensorArray that now not exist
Sensor *_OClSensors = 0;
Sensor *_VibSensors = 0;
Sensor *_HumSensors = 0;
byte _counter = 0; // round robin for advertisment
MsgHdr _msgHdr;
};
join class
Class Join
class Join {
public:
byte Data[ MAXDATASIZE ] {0}; // may 32 fragment use 8’192 increase if BBS must fullfill all fragments
Join();
int Add( byte msg[], int len);
bool IsLast() ;
int GetLength();
bool CheckLast(byte first);
void Reset();
private:
int error = 0; // sequenz is wrong. Reset when the 'last' is arived
int Length = 0; // also pointer to end of message
byte Sequenz = 0; // fragment number. if not eq the spec says throw awai all.
bool Last = false; // last fragment is arrived
};
Join verbindet message Fragment damit eine vollständige Meldung an den Disasembler übergebn werden kann. Damit die Zähler und Speicher global besser abgekapselt sind habe ich sie in eine Classe untergebracht. Jedes Bluetooth Paket hat ein Splittheader, Heder und mind 1 Parameter und kann max 256 byte gross sein. Eine Meldung kann aber theoretisch 8192 byte gross sein (Max32Fragemnt x256Byte.) Es wird so lange zusammengesetzt bis eine paket mit dem last Bit ankommt. Dabei wird die Sequenznumer geprüft. Falls sie nicht stimmt wird alles gelesen bis zum last und dann weggeschmissen.
Anwendung von Join
in main.cpp Function bssControllPointWritten
/// @brief This callback is excecuted whenever the character is written by the peripheral.
/// It does disassembling the datastream and build the coresponding response.
/// @param central is the central that the characteristc belongs.
/// @param characteristic is the character of hte central that has been written
void bssControllPointWritten(BLEDevice central, BLECharacteristic characteristic) {
int sTyp[] = {PARVALTYPSOCL,PARVALTYPSHDE,PARVALTYPSVIP,PARVALTYPMOCL,PARVALTYPMHDE,PARVALTYPMVIP,240};
byte b[256] = {0};
byte *ptBuffer = &b[0];
int len = 0;
int cmd;
int idx ;
if (characteristic.valueLength() > 0) {
len = characteristic.readValue(ptBuffer, 256);
JoinFragment.Add(ptBuffer, len);
// Serial.print("the value"); for (byte k = 0 ; k < len; k++) { Serial.print(ptBuffer[k]); }
// Serial.print("the value"); for (byte k = 0 ; k < len; k++) { Serial.print(b[k]); }
// Serial.println();
} else {
// Serial.println("Callback can't read");
return ;
}
int datalength = JoinFragment.GetLength();
if (JoinFragment.IsLast() && datalength > 0){
// Serial.print("Message Complet (len): "); Serial.println(JoinFragment.GetLength());
int result = binarySensor.DisasemblingControlCommand(0, JoinFragment.Data, datalength);
// Serial.print("result of disa: "); Serial.println(result);
if (result > 0) {
cmd = result /10;
idx = result %10;
if (cmd == 1) binarySensor.CreateGetSensorStatusResponse(sTyp[idx], bssResponseChar);
else
if (cmd == 2) binarySensor.CreateSettingSensorResponse( sTyp[idx], bssResponseChar);
}
}
}
Verbindung via USB zum XIAO-NRF52840 ist manchaml etwas mühsam:
- Wenn die MCU crashed dann ist das Comport locked. 2x Reset auf der MCU hilft dann. Wenn nicht, kann es sein, dass Windows die MCU als Device E: Verbunden hat. Dies wäre gut um die Firmware zu aktualisieren. Beim Download muss der Device im Window entfernt sein.
- In der Regel reicht es, wenn der Download nicht geht, dass man alle COM-Verbindungen löscht (rechts auf Müllkübel clicken).
- ISR on DigitalIO on Change machte mir mühe: